
When you make two vertices connect, a line will be formed. Line: The line data type usually contains two or more vertices (the letters or edges). If you do not have a lot of time, point is the data type that takes the least amount of time, but it is not recommended for large scale maps. Point features consist of X, Y, and, sometimes, Z coordinates. Point works best depending on how far you are from the specific feature, how much time you have, and the type of feature that you are wanting to put on your GIS application. Point: Using point for your vector data is your decision to make. By watching this video, you will learn how vector data is structured, how vector features are created, the object model of vector data, and the precision of vector calculations. If you are interested in learning more about GIS vector data, Civil Gem offers an excellent video on their YouTube Channel. This type of data is tedious and does require careful, detail oriented data collection. It also needs to be constantly updated to remain up to date, reliable, and accurate. It also can be used to answer difficult questions without going to the landscape site.ĭisadvantages: A common disadvantage of vector data is that it can be collected at different scales which may interfere with the process and its accuracy.

The different types of vector data are point, line, or polygon.Īdvantages: An advantage of vector data is that it can be used to map out an entire landscape as well as its features. The geometry typically consists of vertices, which are X, Y, and Z coordinates and form into specific landscape features. This can help individuals answer the following questions: where is the best place to put a business in the area, how many houses are at risk of a flood, how many people live in this specific area, and more.įormats: Vector data usually is represented by using geometry. Main Purpose/ Specification: The main purpose is to be able to add everything that the human eye can see in a visual location to a GIS application. This means that anything that you can visually see in a landscape, such as trees, houses, and rivers, can be represented in a GIS application. What exactly is the vector type of data?ĭefinition: Vector data is the process of representing real world objects and features within the GIS field. This data is continuously being assessed and evaluated in a variety of different fields, but GIS experts are more prominent users of the term. Spatial data is important, as it is data that contains information about locations on the surface of the Earth. Metadata consists of information involving scale, accuracy, projection, data source, manipulations, and how the data is obtained.įor the purpose of this article, I will be focusing solely on spatial data since it involves vector and raster data. It provides characteristics about the spatial data. Attribute data is made up of details such as the information that explains “where”, “what”, and “why”. Vector data, raster data, images, Triangular Irregular Networks (TINs), and terrain datasets are all apart of Spatial data. There are three different types of GIS data, which include spatial, attribute, and metadata. What are the different types of GIS data?

I will also offer links to various YouTube videos in case you need to visually see the difference of vector data vs raster data. In this article, I will provide details about the two different types of data, give reviews about the data’s types, explain what makes them different, and more. Select Raster Processing when needed to correct issues with print output, for example, when a page prints blank or some elements are missing from the print-out.You may be interested to know more about vector and raster data. To improve performance when printing from Revit, reduce or eliminate these conditions in the views to be printed.īecause Revit automatically uses raster processing for views that require it, select Vector Processing for most print jobs to realize the benefits of that technology. Raster processing times depend on the dimensions of the view and the amount of graphics.
Revit automatically uses raster processing for a view if any of the following conditions are true:

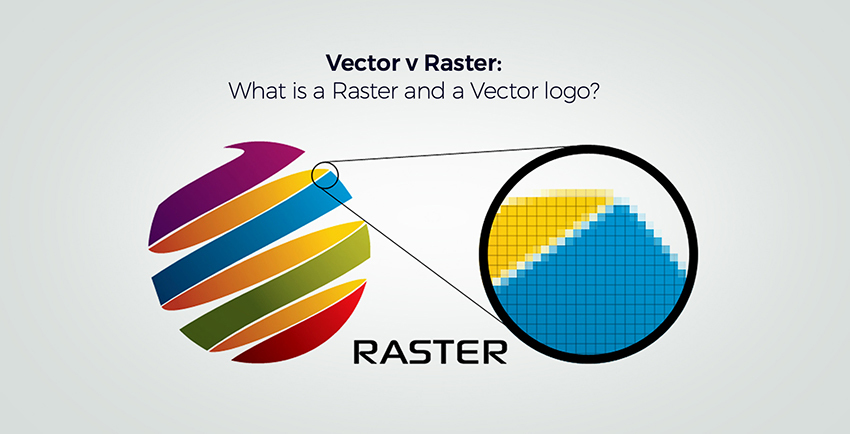
However, some print jobs require raster processing. Raster processing typically produces lower quality output than vector processing. When you zoom into the image, you can see its individual pixels. Raster images consist of individually drawn pixels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
